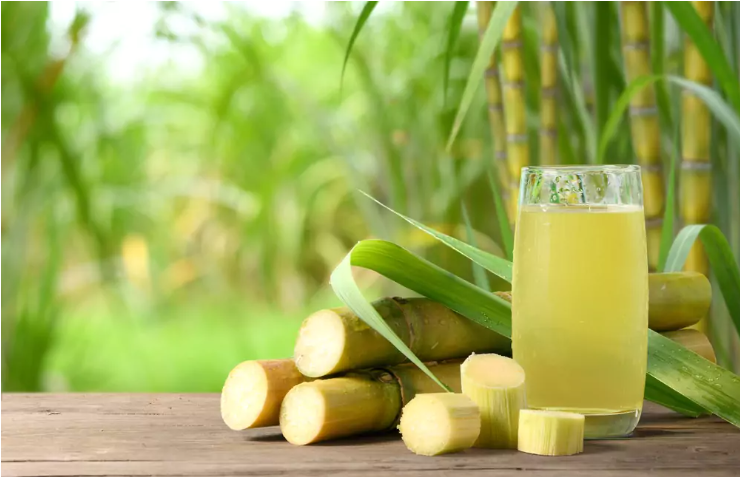
Crisp and sweet, with a bite that lingers on your tongue long after the last swallow, sugarcane, a name synonymous with sugar itself, is a global powerhouse. From fueling morning cups of coffee to gracing desserts with their golden sparkle, it's woven into the fabric of our everyday lives. But beneath its sugary exterior lies a hidden truth, a botanical mystery that has many scratching their heads. Is it grass, a reed, or something else entirely? Fear not, curious minds, for this is a journey to unveil the true nature of this sweet enigma.
Often mistaken for a towering reed, sugarcane, despite its grassy appearance, belongs to a surprising family the Poaceae. Yes, you read that right—the same family that houses familiar faces like wheat, oats, and even bamboo! While its resemblance to reeds may be uncanny, the intricate dance of its internal anatomy reveals a fascinating truth. So, put down your sugar shaker and prepare to embark on a botanical adventure as we peel back the layers of sugarcane's identity and explore the world of grasses in all their surprising diversity.
This journey is not just about satisfying scientific curiosity; it holds practical significance as well. Understanding sugarcane's true classification can inform cultivation practices, pest control strategies, and even breeding programs aimed at maximizing its yield and sweetness. So buckle up and grab your magnifying glass, for we're about to dive deep into the fascinating world of sugarcane and unravel the mystery of its botanical roots.
What Is Sugarcane?
Sugarcane, a towering titan in the realm of sweet things, is more than just a source of table sugar. Its verdant stalks, kissed by the sun and brimming with sucrose, paint a vibrant picture of tropical beauty. Imagine stalks reaching up to 6 meters, like green-armored knights jousting for sunlight. These jointed, fibrous pillars store nature's candy, a testament to sugarcane's impressive growth habit.
Sugarcane thrives in warm, sunny climes, where monsoon rains and fertile soil nourish its thirst for life. From the verdant landscapes of India to the sugarcane prairies of Brazil, it paints tropical and subtropical regions with its sweet symphony. This sun-worshipper wasn't always a global citizen, though. Its origins trace back to New Guinea, where it sweetened the ancient palate as early as 8,000 years ago. Trade winds whispered their secrets, propelling sugarcane across the Indian Ocean and eventually landing it in the hands of Persian and Chinese civilizations. From there, it embarked on a remarkable journey, crossing oceans and continents, tantalizing taste buds, and fueling empires.
Today, a diverse team of sugarcane species plays a starring role in global sugar production. Saccharum officinarum, the "noble cane," boasts the highest sugar content, while Saccharum barberi offers impressive disease resistance. Saccharum spontaneum, the wild progenitor of all cultivars, still whispers tales of its ancient past in the jungles of Southeast Asia. And let's not forget Saccharum hybrids, the powerhouses of the modern sugar industry, combining the best traits of their ancestors to deliver bountiful harvests.
Understanding Botanical Classifications
The verdant world is a symphony of shapes and flavors, but beneath the surface lies a complex language of classification. Fruits, vegetables, and grasses might seem distinct on our plates, but in the botanical kingdom, their identities can blur. So, let's embark on a journey to decode this botanical puzzle and shed light on the fascinating differences between these seemingly disparate plant groups.
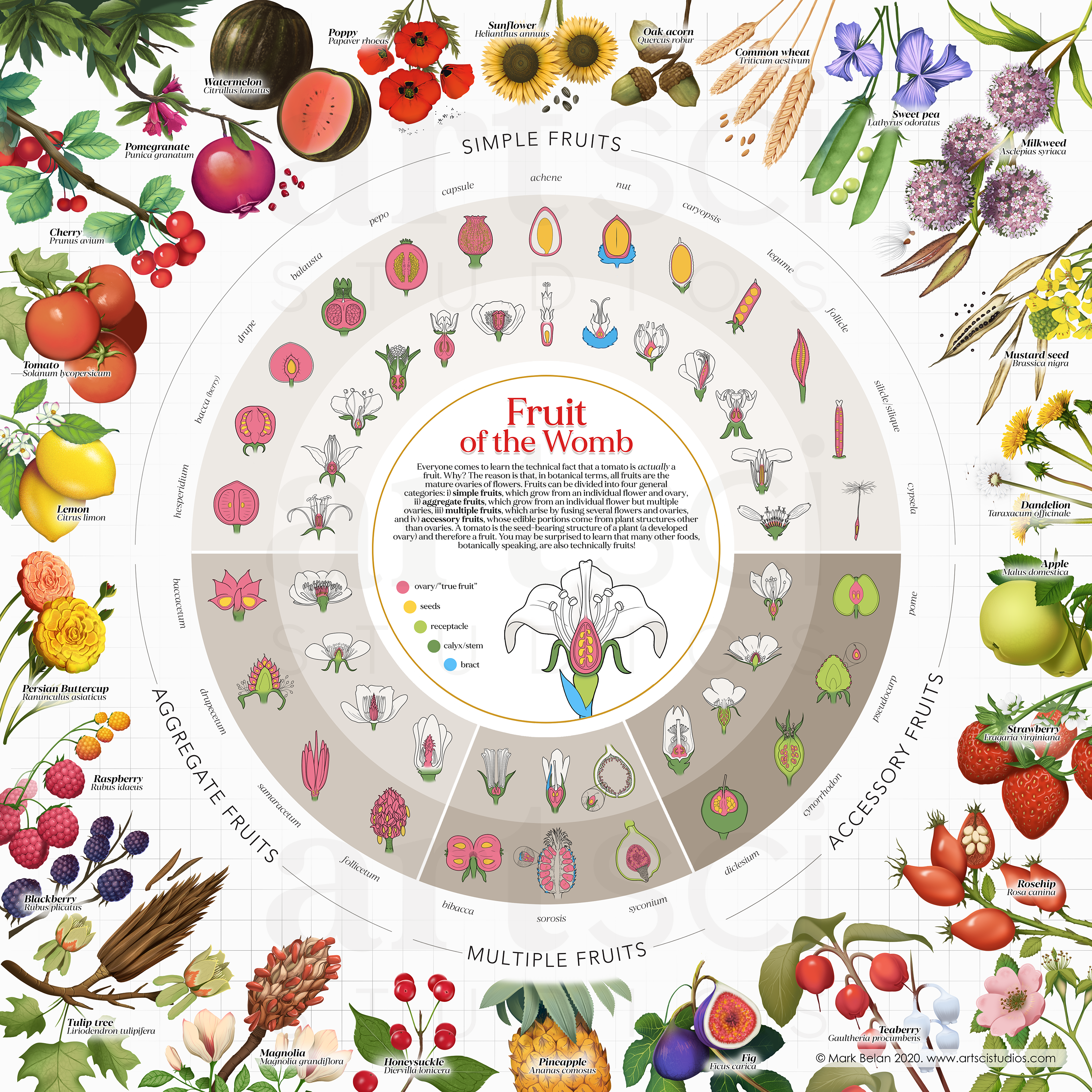
- Fruits -Nature's sweet rewards, fruits, arise from the ripened ovary of a flower. This succulent treasure chest cradles seeds, ensuring their dispersal and future generations. Think of juicy berries, blushing apples, and vibrant oranges—all testaments to the diverse forms fruits can take.
- Vegetables -Ah, the culinary enigma! Vegetables encompass an eclectic bunch, but botanically, they're not a unified group. Instead, they represent edible plant parts, from juicy tomato flesh (fruit!) to sturdy carrot roots (taproot) and leafy greens like spinach (leaves). This diverse ensemble showcases the botanical world's bounty.
- Grasses -Now, let's step into the swaying world of grasses. Imagine slender culms with alternating leaves, topped with inflorescences like feathery plumes or delicate oats. Unlike fruits, where the flower's ovary becomes fleshy, grasses develop dry, one-seeded fruits called caryopses. Think wheat, rice, and bamboo—all members of this ubiquitous family.
But how do botanists organize this vibrant green cast? Plants are categorized based on a set of characteristics, like
- Seed development -How are seeds formed and protected? Fruits boast fleshy or dry structures derived from the flower's ovary, while grasses have single-seeded caryopses.
- Plant structure -From towering trees to creeping vines, plant morphology provides clues. Grasses, for example, exhibit distinct nodes and alternating leaves, while fruits and vegetables often show diverse forms.
- Reproduction -How do plants ensure their offspring's survival? The pollination mechanisms and seed dispersal strategies employed by each group offer valuable insights.
Understanding these differences allows us to appreciate the intricate tapestry of life on Earth. It's not just about sorting plants into neat boxes; it's about deciphering their evolutionary history, predicting their behavior, and ultimately recognizing the delicate balance that sustains our planet's green symphony.
Is Sugarcane A Fruit, Vegetable, Or Grass?
The tall, green stalks of sugarcane may tantalize with their sugary whispers, but its true botanical identity remains a source of confusion. Is it a luscious fruit, a sturdy vegetable, or a swaying grass? To unveil its secret, we must compare its characteristics to the definitions we established earlier.
- Fruits -Nature's candy, fruits, arise from ripened ovaries, cradling seeds within their succulent flesh. Think of a sun-drenched mango, a crimson pomegranate, or a juicy blueberry. While sugar cane boasts sweetness, its fibrous stalks aren't derived from a ripened ovary. Instead, they're modified stems packed with sugar-storing tissues. Unlike the seeds nestled within true fruits, sugarcane seeds are dry and housed within a chaffy exterior, far removed from the succulent flesh.
- Vegetables -The culinary chameleon, vegetables, encompasses diverse edible plant parts. Consider the vibrant pigments of a bell pepper (fruit!), the earthy depths of a beetroot (taproot), or the leafy symphony of kale (leaves). However, sugar cane doesn't neatly fit into any of these categories. Its stalks aren't leaves, fruits, or roots, making it an outsider in the vegetable kingdom.
- Grasses -Now, we enter the swaying realm of grasses. Picture the feathery plumes of wheat, the delicate blades of rice, or the sturdy culms of bamboo. Grasses share several key features: slender, jointed stems with alternating leaves and dry, one-seeded fruits called caryopses. Remarkably, sugarcane ticks all these boxes. Its tall, jointed stalks with alternating leaves bear a striking resemblance to its grassy brethren. More importantly, its seed structure perfectly aligns with the caryopsis, the hallmark of the grass family.
Therefore, despite its sugary nature and culinary prominence, the evidence leans decisively towards sugarcane's grassy identity. Its stem structure, leaf arrangement, and caryopsis-like seed all echo the distinct traits of its grassy kin. While its sweetness may lead us astray, the botanical facts speak for themselves: sugarcane is undeniably a member of the Poaceae family, the proud lineage of grasses, gracing our tables and fueling our world with its sun-kissed sweetness.
Health Benefits And Nutritional Value
Sugarcane, the sun-kissed source of our table sugar, might seem like a simple treat. But beneath its saccharine surface lies a surprising spectrum of nutrients and potential health benefits. So, let's peel back the layers of sugarcane and explore its nutritional value and impact on our well-being.
Fueling the Body -One serving of sugarcane juice (around 28 grams) packs a modest punch of 113 calories, primarily from naturally occurring sugars. While not a powerhouse of protein or fat, it offers a decent dose of essential vitamins and minerals:
- Vitamin B1 (thiamine) -is crucial for energy production and brain function.
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) -aids in metabolism and red blood cell formation.
- Magnesium -supports muscle function and blood pressure regulation.
- Iron -is necessary for oxygen transport and red blood cell production.
- Potassium -maintains healthy electrolyte balance and blood pressure.
These nutrients make sugarcane a potential source of energy, especially for athletes or those seeking a natural sugar boost. Additionally, some studies suggest potential benefits like:
- Aiding digestion -Sugarcane juice contains soluble fiber, which can regulate bowel movements and promote gut health.
- Boosting immunity -Its vitamin C content might offer some immune system support.
- Liver health -Certain antioxidants in sugarcane juice may offer some liver-protective properties.
A Spoonful of Caution -However, overindulging in sugarcane poses its own set of risks:
- High sugar content -The concentrated sugars in sugarcane juice can lead to weight gain, blood sugar spikes, and an increased risk of diabetes if not consumed in moderation.
- Dental health -Sugary foods can promote tooth decay, so proper oral hygiene is important after consuming sugarcane.
- Digestive issues -Excessive intake of fiber can cause bloating and gas in some individuals.
Therefore, enjoying sugarcane within a balanced diet, preferably in its whole form rather than extracted juice, is key to reaping its potential benefits while minimizing risks.
A Final Bite Sugarcane, from its humble stalk to its hidden nutrients, presents a fascinating story of natural sweetness and potential health benefits. By understanding its nutritional value and practicing moderation, we can enjoy this sun-kissed treat as part of a healthy and balanced diet.
Environmental Impact Of Sugarcane Cultivation
Sugarcane, the source of our beloved table sugar, fuels our kitchens and sweetens our lives. But its journey from field to cup comes with environmental costs that cannot be ignored. Let's delve into the impact of sugarcane cultivation, exploring its land use, water consumption, and effects on biodiversity, while also highlighting promising practices and innovations promoting sustainability.
Land Use A Balancing Act
Sugarcane demands fertile land, often leading to deforestation and the conversion of natural habitats. This can disrupt ecosystems, diminish biodiversity, and contribute to soil erosion.
However, sustainable practices like agroforestry, where trees are intercropped with sugarcane, can help protect natural habitats and improve soil health. Additionally, utilizing marginal lands unsuitable for other crops can minimize deforestation pressure.
Water Wars Quenching Thirst Responsibly
Sugarcane is a thirsty crop, requiring significant water for irrigation. This can deplete water resources, especially in arid regions, affecting communities and ecosystems dependent on them.
Precision irrigation techniques, using sensors and drip systems, can optimize water usage and significantly reduce waste. Additionally, utilizing rainwater harvesting and treating wastewater for irrigation can further minimize reliance on freshwater resources.
Biodiversity Blues Protecting The Web Of Life
Intensive sugarcane monocultures offer limited habitat for diverse species. Additionally, the use of pesticides and herbicides can harm beneficial insects and disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Encouraging natural predators and promoting biodiversity through diverse crop rotations and buffer zones can create a more welcoming environment for various species. Utilizing organic farming practices can also reduce reliance on harmful chemicals, protecting both wildlife and human health.
Green Innovations Sweetening The Future
The world of sugarcane farming is embracing exciting innovations to minimize its environmental footprint. These include
- Genetically modified sugarcane varieties -With enhanced drought tolerance and disease resistance, these varieties can reduce water consumption and reliance on pesticides.
- Bioenergy from sugarcane waste -Bagasse, the fibrous residue left after sugar extraction, can be used to generate biofuels, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and creating a circular economy.
- Carbon capture and storage -Sugarcane's ability to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere makes it a potential tool for mitigating climate change.
A Spoonful Of Responsibility Our Choices Matter
As consumers, we hold the power to influence the future of sugarcane cultivation. Choosing products from sustainably certified farms, reducing sugar consumption, and supporting alternative sweeteners can send a strong message to the industry to embrace responsible practices.
By acknowledging the environmental impact of sugarcane and advocating for sustainable practices, we can ensure that our sweet indulgences don't come at the cost of our planet's well-being. Let's work together to cultivate a future where sweetness and sustainability go hand in hand, ensuring a vibrant planet and delicious treats for generations to come.
Remember, every choice we make, from the supermarket aisle to our daily habits, can contribute to a more sustainable future. So, let's savor our sugarcane with a mindful bite, aware of its journey, and committed to supporting practices that ensure sweetness without sacrificing the health of our planet.
Conclusion
Sugarcane, the sun-kissed source of our table sugar, stands at a crossroads. Its journey from field to cup offers a delicious reward but also carries environmental costs we cannot ignore. To ensure a future where sweetness thrives alongside sustainability, we must embrace change. The land needs protection, not depletion. Water must be used wisely, not squandered. Biodiversity cannot be sacrificed for monoculture.
Innovations hold promise, from drought-resistant varieties to bioenergy initiatives. Consumer choices matter, influencing the market towards responsible practices. This is not just about sugarcane; it's about the delicate balance of our planet. Every spoonful becomes a choice, an opportunity to advocate for a future where sweet indulgence and environmental well-being go hand in hand.
Let's savor our sugarcane with mindful bites, supporting practices that ensure sweetness for generations to come. In the end, a sustainable future for sugarcane isn't just about the taste; it's about cultivating a world where nature and our sweet desires can flourish together.